Search:
Petfinder: Urgent Need for Pet Adoption – Find Dogs & Cats
With more adoptable pets than ever, we have an urgent need for pet adopters. Search for dogs, cats, and other available pets for adoption near you.
The Animal Foundation: Animal Shelter and Low-Cost Vet Clinic
The Animal Foundation in Las Vegas is Nevada’s largest animal shelter where you can adopt a pet, find lost dogs and cats, visit our low-cost vet clinic
MSPCA at Northeast Animal Shelter
Ready to adopt? Check out all the animals we have currently available for adoption in Salem. Wonderful pets waiting for wonderful homes!
Save 60% on Animal Shelter on Steam
Your main goal? Finding a suitable home for your pets! Take pictures. Who doesn’t love taking pictures of their pets? We provide you with your own photo room
Adoption Search
Our database is regularly updated throughout the day and contains all of our adoptable pets, including pets with special needs or advanced considerations.
Fairfax County Animal Shelter
The Fairfax County Animal Shelter (FCAS) is Fairfax County’s only open-access, municipal animal shelter. With 4,000 to 5,000 companion animals entering
Cheyenne Animal Shelter
800 Southwest Dr. Cheyenne, WY 82007 (307) 632-6655 © Cheyenne Animal Shelter. Site design by Prairie Sage Creative.
Foothills Animal Shelter | Animal Shelter | Dog & Cat Shelter
As the only full-service animal shelter serving Jefferson County, Colorado, we collaborate with our community to improve the lives of thousands of pets each
Santa Fe Animal Shelter: Home
At Santa Fe Animal Shelter, we believe every animal deserves a safe, loving place to call home. Right now, over 325 animals are under our roof
Los Angeles County Animal Care
Directions. The animal care center is located between Main Street and Broadway two blocks south of the 91 freeway. *Please note: Victoria Street is the same as
The Importance of Animal Shelters
Animal shelters play a vital role in communities by providing safe havens for animals in need, addressing overpopulation issues, and educating the public on responsible pet ownership. They serve as a refuge for homeless and abandoned animals, work to reduce stray populations, and promote animal welfare through various initiatives. Understanding their importance helps us appreciate the efforts made to ensure the well-being of animals and the communities they inhabit.
Protecting Homeless and Abandoned Animals
Animal shelters are often the first line of defense for animals that have been abandoned, lost, or mistreated. They provide essential services that safeguard these animals and give them a second chance at life.

Causes of Animal Homelessness
Several factors contribute to animal homelessness, including abandonment by owners, stray animals born on the streets, and pets lost during disasters. Economic hardships, such as unemployment or housing issues, can lead owners to surrender their pets. Additionally, lack of access to spay and neuter services results in unwanted litters. According to the ASPCA, approximately 6.3 million companion animals enter U.S. animal shelters nationwide every year due to these and other factors.
Intake and Assessment Procedures
When an animal arrives at a shelter, it undergoes a comprehensive intake process. This includes a health examination to check for illnesses or injuries, vaccinations to prevent the spread of diseases, and behavioral assessments to determine temperament. Microchipping is also performed or checked to identify if the animal has an owner. These procedures are crucial for providing appropriate care and increasing the chances of reuniting lost pets with their families or finding new homes. The Humane Society of the United States offers detailed insights into what happens during the intake process.
Rehabilitation and Rehoming Efforts
After assessment, animals may require medical treatment or behavioral rehabilitation. Shelters provide necessary veterinary care, and some have programs to address behavioral issues through training and socialization. The goal is to prepare animals for adoption by enhancing their health and behavior. Shelters then actively work to find suitable homes through adoption events, online listings, and partnerships with rescue organizations. The Best Friends Animal Society is an example of an organization that collaborates with shelters nationwide to promote adoption and reduce euthanasia rates.
Reducing Overpopulation and Stray Issues
Overpopulation of stray animals is a significant concern that affects public health, safety, and the environment. Animal shelters play a key role in mitigating these issues through various programs and community initiatives.
Impact of Overpopulation on Ecosystems
An excess of stray animals can disrupt local ecosystems by preying on wildlife, spreading diseases, and competing with native species for resources. For instance, feral cats are known to have a substantial negative impact on bird populations. The American Bird Conservancy reports that outdoor cats kill an estimated 2.4 billion birds annually in the United States. Overpopulation also leads to increased human-animal conflicts and can strain municipal resources.

Spay and Neuter Programs
Spaying and neutering are effective strategies to control animal populations humanely. Shelters often offer low-cost or free spay and neuter services to the community. By preventing unwanted litters, these programs reduce the number of animals that end up homeless or in shelters. Organizations like SpayUSA provide resources to locate affordable spay/neuter services nationwide, highlighting the importance of these procedures in combating overpopulation.
Community Involvement in Population Control
Community engagement is essential in addressing overpopulation. Shelters collaborate with local residents, volunteers, and organizations to implement Trap-Neuter-Return (TNR) programs for feral cats, which involve humanely trapping, sterilizing, and returning cats to their habitats. Public education campaigns inform citizens about responsible pet ownership and the benefits of spaying/neutering. The Alley Cat Allies organization advocates for TNR and provides resources for communities to manage feral cat populations effectively.
Promoting Animal Welfare and Education
Animal shelters extend their impact beyond immediate animal care by promoting welfare and education initiatives. These efforts aim to foster a compassionate community that values and respects animal life.
Public Awareness Campaigns
Shelters conduct public awareness campaigns to highlight issues such as adoption, spaying/neutering, and preventing animal cruelty. These campaigns utilize various media platforms to reach a wide audience, encouraging community members to participate in animal welfare efforts. For example, the Shelter Pet Project is a public service campaign that encourages adopting pets from shelters and rescue groups.
Educational Programs in Schools
Integrating animal welfare education into school curriculums helps instill compassion and responsibility in younger generations. Shelters may offer classroom presentations, educational materials, and interactive experiences with animals. These programs teach students about humane treatment, the role of shelters, and how to care for pets. Resources from organizations like TeachKind provide educators with lesson plans and activities focused on kindness to animals.
Workshops on Responsible Pet Ownership
Shelters often host workshops and seminars for the public on topics such as basic pet care, training, and understanding animal behavior. These workshops empower pet owners with knowledge to prevent common issues that lead to pet surrender, such as behavioral problems or unexpected health expenses. By promoting responsible ownership, shelters aim to reduce the number of animals needing their services. The American Veterinary Medical Association offers guidelines and resources that are frequently shared during such educational events.
Types of Animal Shelters
Animal shelters vary widely in their structures, funding sources, and operational philosophies. Understanding these differences is crucial for appreciating how each type contributes uniquely to animal welfare. This section delves into the various kinds of animal shelters, including public (municipal) shelters, private and non-profit shelters, no-kill and open-admission shelters, as well as rescue groups and sanctuaries.
Public (Municipal) Shelters
Public or municipal shelters are government-funded facilities tasked with animal control and public safety responsibilities within their jurisdictions. They are often the primary agencies handling stray, abandoned, and lost animals in a community.
Funding and Resource Allocation
Municipal shelters receive funding from local government budgets, which are derived from taxpayer dollars. These funds cover operational costs such as staff salaries, facility maintenance, animal care, and enforcement of local animal ordinances. However, budget limitations often mean these shelters operate with constrained resources. According to the National Animal Care & Control Association (NACA), many municipal shelters face financial challenges that impact their ability to provide comprehensive services.
Services Provided to the Community
Public shelters offer a range of essential services, including:
- Animal Control Enforcement: Responding to reports of stray or dangerous animals, investigating cruelty cases, and enforcing licensing laws.
- Sheltering: Providing temporary housing for lost, abandoned, or surrendered animals.
- Adoption Programs: Facilitating the adoption of animals to suitable homes.
- Public Education: Offering information on responsible pet ownership and local animal regulations.
For example, Los Angeles Animal Services provides community programs such as low-cost vaccination clinics and spay/neuter services to reduce pet overpopulation.
Challenges Unique to Public Shelters
Municipal shelters often grapple with specific challenges:
- Overcrowding: High intake rates can lead to overcrowded facilities, affecting animal welfare and increasing the risk of disease transmission.
- Limited Funding: Dependence on government budgets may result in insufficient funds for necessary resources and staffing.
- Policy Constraints: Required to accept all animals (open-admission), they may face tough decisions regarding euthanasia due to space or behavioral issues.
These challenges underscore the need for community support and effective management strategies to improve outcomes for animals in municipal shelters.
Private and Non-Profit Shelters
Private and non-profit shelters operate independently of government control, relying heavily on community support to fulfill their missions. They often have more flexibility in their policies and programs compared to municipal shelters.
Role of Donations and Grants
These shelters depend on donations from individuals, businesses, and grants from foundations to fund their operations. Financial contributions support:
- Animal Care: Providing food, medical treatment, and shelter for animals.
- Facility Upkeep: Maintaining and improving shelter facilities.
- Programs and Services: Implementing adoption events, educational outreach, and spay/neuter initiatives.
Organizations like the Petco Love Foundation offer grants to support the lifesaving work of animal welfare groups across the country.
Volunteer Contributions
Volunteers are vital to private shelters, offering their time and skills to:
- Animal Socialization: Interacting with animals to improve their adaptability and reduce stress.
- Administrative Tasks: Assisting with clerical work, fundraising, and event planning.
- Community Outreach: Educating the public and promoting the shelter’s mission.
The ASPCA highlights how volunteer involvement enhances the quality of life for shelter animals and expands the organization’s capacity to serve more animals.
Special Programs and Initiatives
Private shelters often implement innovative programs to address specific needs:
- Behavioral Training: Providing specialized training to help animals overcome behavioral issues, increasing their chances of adoption.
- Foster Care Networks: Placing animals in temporary homes to alleviate shelter overcrowding and give personalized care.
- Humane Education: Offering workshops and resources to educate the public on animal welfare topics.
For instance, the Animal Humane Society offers a variety of community programs, including pet loss support groups and youth volunteering opportunities.

No-Kill and Open-Admission Shelters
Shelters are often categorized based on their intake policies and approaches to euthanasia, leading to distinctions between no-kill and open-admission facilities.
Philosophies Behind No-Kill Policies
No-kill shelters strive to save all healthy and treatable animals, typically aiming for a save rate of 90% or higher. Euthanasia is reserved only for animals with incurable illnesses or severe behavioral issues that prevent them from being safely rehomed. Organizations like the Best Friends Animal Society advocate for no-kill initiatives, providing resources and support to help shelters achieve these goals.
Managing Limited Admissions
Many no-kill shelters are limited-admission, meaning they accept animals based on their capacity to provide adequate care. This approach helps maintain high-quality care but may result in waiting lists or referrals to other facilities. Managing admissions involves careful assessment of each animal’s needs and the shelter’s resources.
Ethical Considerations and Debates
The no-kill movement has sparked ethical discussions within the animal welfare community. Key considerations include:
- Resource Allocation: Balancing the allocation of limited resources between saving individual animals and addressing broader community needs.
- Impact on Other Shelters: Limited-admission policies may place additional burdens on open-admission shelters that cannot turn away animals.
- Quality of Life: Ensuring that animals kept long-term in shelters receive proper enrichment and do not suffer from prolonged confinement.
The Humane Society of the United States provides insights into these debates, emphasizing the importance of collaboration and comprehensive strategies to reduce euthanasia rates.
Rescue Groups and Sanctuaries
Rescue groups and sanctuaries focus on specific populations of animals, offering specialized care and often providing lifelong sanctuary to those who cannot be adopted.
Specialization in Breeds or Species
Many rescue groups concentrate on particular breeds, species, or categories of animals, such as:
- Breed-Specific Rescues: Dedicated to rescuing and rehoming specific breeds, like Labrador Retriever Rescue.
- Wildlife Rehabilitation Centers: Focused on rehabilitating injured or orphaned wildlife for release back into their natural habitats.
- Exotic Animal Sanctuaries: Providing care for exotic pets that have been surrendered or seized due to illegal ownership.
Specialization allows these groups to develop expertise in the care, behavior, and needs of specific animals.
Long-Term Care Strategies
Sanctuaries prioritize the well-being of animals that may not be suitable for adoption due to health, behavioral, or legal reasons. Strategies include:
- Creating Naturalistic Environments: Designing enclosures that mimic natural habitats to promote physical and psychological health.
- Individualized Care Plans: Developing care routines tailored to each animal’s needs.
- Lifetime Commitment: Ensuring animals have a permanent home where they can live out their lives safely.
The Farm Sanctuary exemplifies this approach by providing lifelong care to farm animals rescued from abuse and neglect.
Success Stories and Case Studies
Sharing success stories highlights the impact of rescue groups and sanctuaries, inspiring support and demonstrating effective practices. Examples include:
- Rehabilitation Tales: Narratives of animals recovering from trauma or illness, like those shared by the Wildlife Rehabilitation Center of Minnesota.
- Adoption Journeys: Stories of animals finding their forever homes after overcoming challenges.
- Community Impact: Case studies showing how rescue efforts have positively affected local ecosystems or reduced stray populations.
These stories not only celebrate successes but also educate the public on the importance of specialized care and advocacy.

Challenges Facing Animal Shelters
Animal shelters play a crucial role in safeguarding the welfare of animals and supporting communities. However, they often encounter significant challenges that hinder their ability to operate effectively. Limited resources and funding, overcrowding and space constraints, and the need for specialized health and behavioral care are among the primary obstacles these shelters face. Understanding these challenges is essential for developing solutions that enhance the well-being of animals and the efficiency of shelters.
Limited Resources and Funding
Financial constraints are one of the most pressing issues for animal shelters. Operating a shelter requires substantial funding for necessities like food, medical care, facility maintenance, staff salaries, and utilities. Many shelters rely heavily on donations and grants, which can be unpredictable and insufficient to meet all operational needs.
Strategies for Fundraising
To address funding challenges, shelters employ various fundraising strategies:
- Community Events: Hosting events such as charity walks, adoption fairs, and gala dinners engages the community and raises funds. For example, the ASPCA organizes nationwide events to support animal welfare initiatives.
- Online Campaigns: Utilizing crowdfunding platforms like GoFundMe or social media fundraisers expands reach. Shelters can share compelling stories and updates to encourage donations from a broader audience.
- Grant Applications: Applying for grants from organizations dedicated to animal welfare, such as the Petco Love Foundation, can provide significant funding for specific projects or general operations.
- Corporate Partnerships: Collaborating with businesses for sponsorships or matching gift programs can enhance fundraising efforts. Companies may also donate supplies or services, reducing operational costs.
- Membership Programs: Implementing monthly giving programs encourages supporters to provide consistent financial assistance. The Humane Society of the United States offers membership options that fund their ongoing efforts.
Cost-Saving Measures
In addition to fundraising, shelters adopt cost-saving strategies to maximize their limited resources:
- Volunteer Engagement: Recruiting volunteers reduces labor costs and brings diverse skills to the shelter. Volunteers assist with animal care, administrative tasks, and community outreach.
- In-Kind Donations: Accepting donations of food, supplies, and equipment lowers expenses. Many shelters maintain wish lists on their websites or platforms like AmazonSmile Charity Lists for easy donor access.
- Partnerships with Veterinarians: Establishing relationships with local veterinary clinics can lead to discounted or pro bono medical services. Programs like the American Veterinary Medical Foundation’s (AVMF) charitable care support such collaborations.
- Energy Efficiency: Implementing energy-saving measures reduces utility costs over time, allowing funds to be redirected to animal care.
- Bulk Purchasing: Buying supplies in bulk or joining cooperative purchasing groups can result in significant savings.
Impact on Animal Care
Financial limitations can directly affect the quality of care animals receive:
- Medical Treatment: Limited funds may restrict access to necessary medical procedures, vaccinations, or emergency care.
- Staffing Levels: Understaffing due to budget constraints can lead to overworked employees and less individual attention for each animal.
- Facility Maintenance: Insufficient resources may result in outdated or inadequate facilities, impacting animal comfort and health.
- Program Availability: Budget cuts might eliminate enrichment programs or behavioral training that enhance adoptability.
Understanding these impacts highlights the importance of supporting shelters financially to ensure they can provide optimal care.
Overcrowding and Space Constraints
Overcrowding is a significant challenge for many shelters, leading to stressful environments for both animals and staff. Limited space can compromise animal health and hinder the shelter’s ability to accept new animals in need.
Factors Leading to Overcrowding
Several factors contribute to overcrowding:
- High Intake Rates: Seasonal influxes, such as “kitten season,” result in large numbers of animals entering shelters simultaneously.
- Low Adoption Rates: Economic downturns or lack of community awareness can reduce adoption rates, causing animals to stay longer.
- Limited Spay/Neuter Programs: Without effective spay and neuter initiatives, animal populations grow unchecked, increasing shelter intake.
- Natural Disasters: Events like hurricanes or wildfires displace pets, leading to sudden surges in shelter populations.
Effects on Animal Health and Behavior
Overcrowding can have detrimental effects:
- Disease Spread: High-density environments facilitate the transmission of infectious diseases like kennel cough or feline upper respiratory infections.
- Stress and Anxiety: Noise, lack of space, and limited human interaction can cause stress-related behaviors, making animals less adoptable.
- Aggression: Overcrowded conditions may lead to increased aggression among animals due to competition for resources.
- Reduced Quality of Care: Staff may struggle to meet the needs of all animals, leading to neglect of essential care tasks.
The Association of Shelter Veterinarians provides guidelines on managing shelter populations to minimize these risks.
Innovative Solutions to Space Issues
Shelters adopt creative strategies to address overcrowding:
- Foster Programs: Recruiting community members to provide temporary homes for animals reduces shelter populations and offers individualized care. The ASPCA Foster Program is a successful example.
- Transfer Partnerships: Collaborating with other shelters and rescue organizations allows for the transfer of animals to facilities with available space.
- Adoption Incentives: Implementing promotions or reduced adoption fees during peak times can increase adoption rates. Events like Clear the Shelters have nationwide impact.
- Managed Intake: Scheduling owner surrenders and using waitlists help regulate the number of animals entering the shelter at once.
- Facility Expansion: Seeking funding for expansion projects can provide long-term solutions to space limitations.
Health and Behavioral Care for Animals
Ensuring the physical and mental well-being of animals is a core responsibility of shelters. Addressing health issues and providing behavioral support increases the likelihood of successful adoptions.
Common Medical Conditions Addressed
Shelters frequently manage various medical conditions:
- Infectious Diseases: Conditions like parvovirus, distemper, and ringworm are common. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent outbreaks.
- Chronic Illnesses: Animals may suffer from diabetes, heartworm, or kidney disease, requiring ongoing care.
- Injuries: Wounds from accidents or abuse necessitate medical intervention and rehabilitation.
- Parasites: Routine deworming and flea/tick prevention protect individual animals and the shelter population.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) offers resources on managing health risks in shelter environments.
Behavioral Training and Rehabilitation
Behavioral issues can hinder adoption prospects:
- Fear and Anxiety: Previous trauma or the stress of the shelter environment can cause withdrawal or fear-based behaviors.
- Aggression: Lack of socialization or negative experiences may lead to aggressive reactions.
- House Training: Animals may need basic training to become suitable household pets.
Shelters implement programs to address these challenges:
- Behavior Assessments: Evaluations help identify issues and create tailored intervention plans.
- Positive Reinforcement Training: Reward-based methods encourage desirable behaviors and build trust.
- Behavior Modification Programs: Specialized training addresses specific problems like resource guarding or separation anxiety.
The Animal Behavior Society provides expertise and resources for behavioral interventions.
Importance of Mental Stimulation
Mental enrichment is vital for animal welfare:
- Environmental Enrichment: Providing toys, puzzles, and varied environments keeps animals engaged and reduces stress.
- Social Interaction: Regular human contact and opportunities to interact with other animals promote socialization.
- Exercise: Physical activity supports mental health and reduces problematic behaviors.
Implementing enrichment programs enhances quality of life and adoptability. The ASPCA Pro offers guidance on enrichment strategies for shelters.

How Animal Shelters Benefit Communities
Animal shelters are integral to the well-being of both animals and humans within a community. They provide essential services that go beyond simply housing stray or abandoned animals. By facilitating responsible pet adoptions, offering low-cost veterinary services, and educating the public on proper animal care, shelters enhance public health, safety, and foster a compassionate society. This section explores how animal shelters contribute positively to communities through these vital functions.
Facilitating Responsible Pet Adoptions
Animal shelters play a crucial role in connecting animals in need with loving homes. By promoting responsible adoptions, they ensure that pets and owners are well-matched, which increases the likelihood of a permanent and happy relationship.
Adoption Counseling Services
Adoption counseling services are designed to help potential pet owners make informed decisions. Shelter staff or trained volunteers meet with prospective adopters to discuss their lifestyle, expectations, and the responsibilities that come with pet ownership. This personalized approach ensures that the adopter understands the commitment and selects a pet that fits well with their home environment.
For example, the ASPCA provides resources and counseling to assist individuals in choosing the right pet. Counselors may ask questions about the adopter’s daily routine, living situation, and experience with animals to provide guidance tailored to their specific circumstances.
Screening Processes for Adopters
Implementing thorough screening processes helps shelters place animals in safe and suitable homes. This may include:
- Application Forms: Collecting information about the adopter’s history with pets, household members, and living arrangements.
- Interviews: Discussing expectations and addressing any concerns or questions.
- Reference Checks: Contacting personal or veterinary references to verify the adopter’s ability to care for the animal.
These steps are essential to ensure the welfare of the animal and the satisfaction of the adopter. Organizations like the Humane Society of the United States emphasize the importance of responsible adoption practices to prevent animals from being returned to the shelter or placed in unsuitable environments.
Post-Adoption Support
Post-adoption support services are vital in helping new pet owners adjust and address any challenges that may arise. Shelters may offer:
- Behavioral Advice: Guidance on training and dealing with common issues like housebreaking or socialization.
- Medical Information: Resources on vaccinations, spaying/neutering, and general health care.
- Community Connections: Referrals to local veterinarians, trainers, or pet supply stores.
For instance, Best Friends Animal Society provides ongoing support to adopters to ensure a smooth transition. This assistance increases the likelihood of a successful, lifelong adoption by addressing problems early and strengthening the bond between pet and owner.
Providing Low-Cost Veterinary Services
Access to affordable veterinary care is essential for pet owners and benefits the broader community by promoting public health and reducing the spread of diseases.
Affordable Vaccination Clinics
Many shelters host low-cost vaccination clinics to make essential vaccines accessible to all pet owners. Vaccinations protect pets from common diseases and help prevent outbreaks that could affect other animals and humans.
Shelters may offer vaccines for:
- Rabies: A fatal disease transmissible to humans.
- Distemper: A serious viral illness affecting dogs.
- Parvovirus: A highly contagious virus that can be deadly to puppies.
Organizations like Petco Love partner with shelters to provide these services, ensuring pets remain healthy and communities are safeguarded against potential health risks.
Spay/Neuter Assistance Programs
Spaying and neutering are critical in controlling the pet population and reducing the number of animals entering shelters. Shelters often provide these services at a reduced cost or even for free to encourage pet owners to participate.
Benefits of spay/neuter programs include:
- Decreased Overpopulation: Fewer unwanted litters mean fewer animals in shelters.
- Health Improvements: Reduced risk of certain cancers and infections in pets.
- Behavioral Benefits: Can decrease aggression and roaming behaviors.
The ASPCA Spay/Neuter Alliance offers resources and support to shelters implementing these programs, highlighting their importance in community health initiatives.
Microchipping and Identification
Microchipping pets is a reliable method of ensuring lost animals can be reunited with their owners. Shelters provide affordable microchipping services, which involve implanting a small chip under the pet’s skin that contains a unique identification number linked to the owner’s contact information.
According to the American Veterinary Medical Association (AVMA), microchipped dogs are more than twice as likely to be returned to their owners, and microchipped cats are 20 times more likely. This service reduces the number of stray animals and eases the burden on shelters.
Educating the Public on Animal Care
Education is a key component of animal shelters’ missions, aiming to promote responsible pet ownership and enhance the human-animal bond within the community.
Hosting Community Events
Shelters often organize events to engage the public and spread awareness about animal welfare. These events may include:
- Adoption Fairs: Showcasing animals available for adoption and providing information on pet care.
- Workshops and Seminars: Covering topics like obedience training, nutrition, and health care.
- Youth Programs: Educating children about kindness to animals and responsible ownership.
For example, the San Diego Humane Society hosts various community events that not only promote adoptions but also provide valuable educational experiences for attendees.
Distribution of Educational Materials
Providing accessible information helps pet owners make informed decisions about their animals’ care. Shelters distribute materials such as:
- Brochures and Flyers: Covering basic care, signs of illness, and training tips.
- Online Resources: Articles, videos, and webinars available on the shelter’s website.
- Newsletters: Regular updates on shelter activities, success stories, and educational content.
These resources empower individuals to provide better care for their pets and understand the importance of issues like spaying/neutering and vaccinations. The Humane Society Veterinary Medical Association offers a wealth of educational content that shelters can share with their communities.
Collaborations with Local Organizations
Shelters collaborate with schools, businesses, and other nonprofits to broaden their outreach and impact. Partnerships may involve:
- School Programs: Implementing curricula that teach students about animal welfare and empathy.
- Corporate Engagement: Working with companies on volunteer programs or sponsorships.
- Joint Initiatives: Partnering with local governments or environmental groups on projects like community cat management or wildlife conservation.
Such collaborations enhance the shelter’s ability to serve the community effectively. For instance, PAWS Chicago works closely with local organizations to address animal homelessness and promote adoption.

Ways to Support Animal Shelters
Supporting animal shelters is a compassionate way to make a significant impact on the lives of animals and the well-being of your community. Shelters often operate with limited resources and rely heavily on the generosity of volunteers, donors, and advocates to continue their vital work. This section explores various ways you can contribute to animal shelters, whether through volunteering, donating, fostering, or advocating for animal welfare initiatives.
Volunteering Opportunities
Volunteering at an animal shelter offers a hands-on opportunity to directly improve the lives of animals in need. By donating your time and skills, you help shelters operate more effectively and provide better care for their animals. Understanding the different volunteer roles and how to get involved can help you find the best fit for your interests and abilities.
Types of Volunteer Roles
Animal shelters offer a variety of volunteer roles to suit different skills and preferences:
- Animal Care: Assisting with feeding, grooming, and exercising animals to keep them healthy and happy.
- Adoption Support: Helping potential adopters find the right pet by providing information and guidance.
- Administrative Tasks: Supporting shelter operations through clerical work, data entry, and phone support.
- Event Planning: Organizing fundraising events, adoption fairs, and community outreach programs.
- Foster Care: Providing temporary homes for animals that need special attention or relief from the shelter environment.
- Maintenance and Cleaning: Ensuring the shelter remains a clean and safe environment for the animals.
- Marketing and Social Media: Promoting the shelter and its animals through various media channels.
Websites like VolunteerMatch can help you find local shelters and volunteer opportunities that match your interests.
How to Get Involved
Getting started as a volunteer is straightforward:
- Research Local Shelters: Use online directories or community boards to identify shelters in your area.
- Review Requirements: Check the shelter’s website for volunteer requirements, such as age limits or time commitments.
- Apply: Fill out a volunteer application, which may be available online or at the shelter.
- Attend Orientation: Participate in training sessions to learn about the shelter’s policies and procedures.
- Schedule Shifts: Coordinate with volunteer coordinators to find times that fit your schedule.
The ASPCA offers resources and guidance on how to become a volunteer, including what to expect and how to prepare.
Impact of Volunteer Work on Shelters
Volunteers are the backbone of many shelters, and their contributions have a significant impact:
- Enhanced Animal Care: More hands-on deck mean animals receive more attention, socialization, and care.
- Increased Adoption Rates: Volunteers help animals become more adoptable by improving their behavior and exposure.
- Operational Efficiency: Volunteers assist with essential tasks, allowing staff to focus on critical operations.
- Community Engagement: Active volunteers help raise awareness and foster a community that values animal welfare.
According to the Humane Society of the United States, volunteering not only benefits the shelter and animals but also enriches the lives of the volunteers themselves.
Donating Supplies or Funds
Financial contributions and supply donations are crucial for shelters to provide adequate care for their animals. Understanding what shelters need and how your donations are used ensures your support makes a meaningful difference.
Essential Items Needed
Common items that shelters often need include:
- Pet Food: High-quality dog and cat food, including specialty diets.
- Bedding: Blankets, towels, and pet beds to keep animals comfortable.
- Cleaning Supplies: Disinfectants, laundry detergent, and trash bags for maintaining a clean environment.
- Medical Supplies: First-aid kits, medications, and supplements.
- Toys and Enrichment Items: Toys, scratching posts, and chew items to keep animals mentally stimulated.
Some shelters maintain wish lists on platforms like Amazon Smile Charity Lists or their websites, making it easy to see what they currently need.
One-Time vs. Recurring Donations
When considering financial support, you can choose between:
- One-Time Donations: Great for contributing to specific campaigns or responding to immediate needs.
- Recurring Donations: Provide ongoing support, helping shelters plan their budgets and operations more effectively.
Recurring donations can often be set up easily through the shelter’s website or platforms like Network for Good.
Transparency in How Donations Are Used
Ensuring your donations are used effectively is important:
- Review Financial Reports: Nonprofit shelters typically publish annual reports detailing their financials.
- Ask Questions: Contact the shelter directly if you have questions about how funds are allocated.
- Check for Accreditation: Organizations like Charity Navigator evaluate nonprofits for financial health and transparency.
Transparency builds trust and encourages continued support from donors.
Adopting or Fostering Animals
Adoption and fostering are impactful ways to support shelters by providing loving homes for animals. Fostering, in particular, offers temporary care for animals that may not thrive in a shelter environment.
Benefits of Fostering
Fostering animals provides several advantages:
- Eases Shelter Overcrowding: Frees up space and resources for other animals.
- Provides Individualized Care: Animals receive personalized attention, improving their health and behavior.
- Increases Adoption Chances: Fostered animals are often better socialized and can adjust more easily to permanent homes.
- Flexible Commitment: Fostering can be short-term or long-term, depending on your availability.
Organizations like Best Friends Animal Society highlight how fostering saves lives and supports shelters.
Steps to Become a Foster Caregiver
To become a foster caregiver:
- Contact Local Shelters: Inquire about their fostering programs and requirements.
- Complete an Application: Provide details about your living situation and experience with animals.
- Attend Training: Learn about the responsibilities and expectations of fostering.
- Prepare Your Home: Ensure you have the necessary space and supplies.
- Provide Care: Offer a safe, loving environment for the foster animal until they are adopted or ready to return to the shelter.
Resources from Petfinder can guide you through the fostering process.
Stories of Successful Foster Placements
Success stories demonstrate the positive impact of fostering:
- Transformation Journeys: Animals overcoming medical or behavioral challenges in a foster home.
- Foster Failures: When foster caregivers become so attached they adopt the animal themselves.
- Community Inspiration: Sharing experiences can encourage others to consider fostering.
Reading stories on sites like the ASPCA Blog can provide inspiration and insight into the fostering experience.
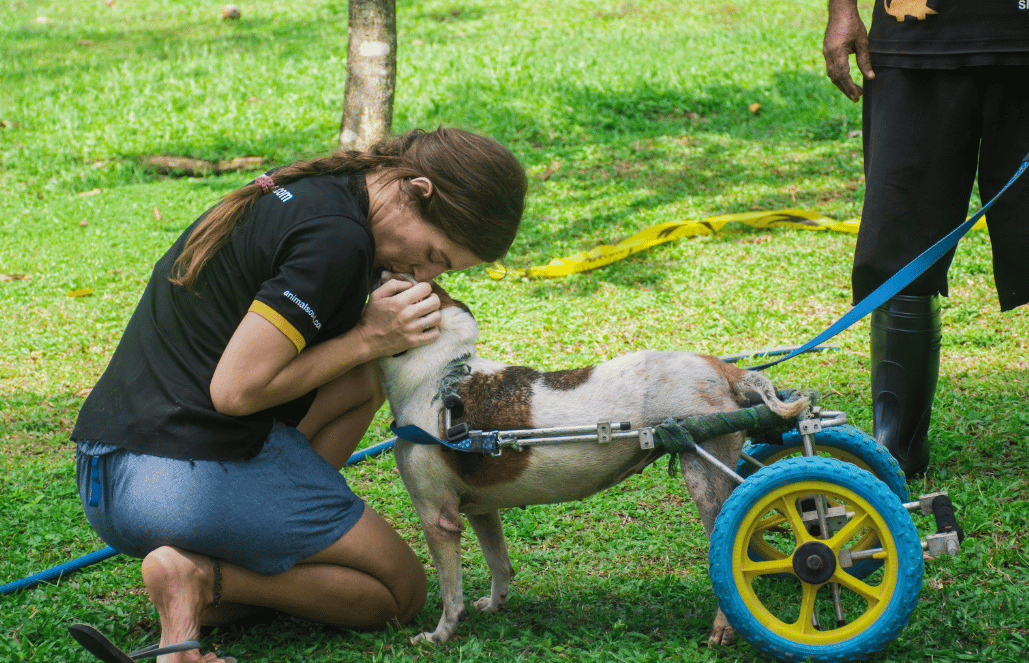
Advocating for Animal Welfare Initiatives
Advocacy efforts help drive systemic change and improve animal welfare on a larger scale. By engaging in policy-making, raising awareness, and mobilizing your community, you can support shelters and animals beyond direct involvement.
Engaging in Legislative Processes
Influencing laws and regulations can lead to significant improvements in animal welfare:
- Stay Informed: Follow legislative developments through resources like the Animal Legal Defense Fund.
- Contact Lawmakers: Reach out to your representatives to express support for animal-friendly legislation.
- Participate in Advocacy Campaigns: Join efforts organized by groups like the Humane Society Legislative Fund.
Your voice can help enact laws that protect animals from cruelty and neglect.
Raising Awareness Through Social Media
Social media is a powerful tool for advocacy:
- Share Information: Post about shelter needs, adoption events, and animal welfare issues.
- Engage with Content: Like, comment, and share posts from shelters and advocacy groups to increase their reach.
- Create Original Content: Share your experiences and encourage others to get involved.
Organizations like Alley Cat Allies provide resources for effective online advocacy.
Organizing Community Support Groups
Building local networks amplifies your impact:
- Form Groups: Start a local club or organization focused on supporting animal shelters.
- Host Events: Organize fundraisers, awareness campaigns, or educational workshops.
- Collaborate: Partner with shelters, veterinarians, and other animal welfare organizations.
Community groups can drive change at the grassroots level, fostering a culture of compassion and responsibility.